Understanding Retinal Detachments: Signs and What You Need to Do
August 20, 2024
Understanding Retinal Detachment: Signs and What You Need to Do
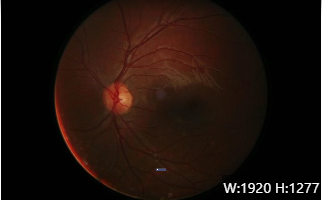
Retinal detachment is a serious eye condition that requires immediate attention. It occurs when the retina, the light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eye, separates from its underlying supportive tissue. Without prompt treatment, it can lead to permanent vision loss. Recognizing the early signs of retinal detachment and knowing what actions to take can be crucial for preserving your vision.
Signs of Retinal Detachment
What to Do If You Suspect Retinal Detachment
Prevention and Risk Factors
While not all cases of retinal detachment can be prevented, being aware of the risk factors can be beneficial. These include:
Regular eye exams are essential, especially if you have any of these risk factors. Early detection of issues like retinal tears can sometimes prevent detachment.
Retinal detachment is a critical eye condition that demands immediate attention. By recognizing the signs early and seeking prompt medical care, you can significantly increase your chances of preserving your vision. Remember, if you experience sudden changes in your vision, don’t wait—contact a healthcare professional immediately. Protecting your eye health is crucial for maintaining your overall quality of life and visual clarity.
Go Back Retinal detachment is a serious eye condition that requires immediate attention. It occurs when the retina, the light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eye, separates from its underlying supportive tissue. Without prompt treatment, it can lead to permanent vision loss. Recognizing the early signs of retinal detachment and knowing what actions to take can be crucial for preserving your vision.
Signs of Retinal Detachment
- Sudden Appearance of Floaters: Floaters are tiny specks or cobweb-like images that drift through your field of vision. While they are common and often harmless, a sudden increase in floaters, especially if they appear in clusters or are accompanied by flashes of light, may be a sign of retinal detachment.
- Flashes of Light: You might see flashes or sparks of light, particularly in your peripheral vision. These flashes occur when the retina is being pulled or stretched. The presence of these flashes, especially if they are new or have changed in nature, warrants immediate medical attention.
- Blurred or Distorted Vision: If you experience sudden blurring or distortion in your vision, it can be a warning sign. This might manifest as a gray or shadowy curtain appearing in your peripheral vision or central vision.
- Loss of Peripheral Vision or curtain like sensation: A loss of side vision or the sensation of a dark curtain or shadow falling over part of your vision could indicate retinal detachment. This loss can progress rapidly, making it crucial to seek help right away.
- Reduced Visual Acuity: If you notice a sudden decline in your ability to see clearly, particularly in one eye, this could be related to a detachment. Any abrupt change in visual acuity should be evaluated by a professional.
What to Do If You Suspect Retinal Detachment
- Seek Immediate Medical Attention: Retinal detachment is a medical emergency. Contact an eye care specialist or visit an emergency room as soon as you notice any of the above symptoms. The sooner the retina is reattached, the better the chances of preserving vision.
- Avoid Rubbing or Pressing on Your Eye: If you suspect a retinal detachment, avoid rubbing or putting pressure on your eye. This can worsen the condition or lead to additional damage.
- Keep Your Head in a Stable Position: Try to keep your head still and avoid sudden movements. This can help prevent further damage or exacerbation of the condition while you arrange for medical care.
Prevention and Risk Factors
While not all cases of retinal detachment can be prevented, being aware of the risk factors can be beneficial. These include:
- Age: The risk increases with age, particularly after 40.
- Eye Injury: Trauma or injury to the eye can increase the risk. If you have an eye injury, its always best to seek medical attention to make sure there is not damage to the eye.
- Previous Eye Surgery: Surgery such as cataract removal may increase susceptibility.
- High Myopia: Severe nearsightedness can stretch and weaken the retina, making patients more susceptible to retinal detachments
- Family History: A family history of retinal detachment can also increase risk.
Regular eye exams are essential, especially if you have any of these risk factors. Early detection of issues like retinal tears can sometimes prevent detachment.
Retinal detachment is a critical eye condition that demands immediate attention. By recognizing the signs early and seeking prompt medical care, you can significantly increase your chances of preserving your vision. Remember, if you experience sudden changes in your vision, don’t wait—contact a healthcare professional immediately. Protecting your eye health is crucial for maintaining your overall quality of life and visual clarity.